The case for Neuromorphic Computing
- Daniel Ezekiel
- Apr 11, 2025
- 3 min read

Introduction
Neuromorphic computing is an innovative approach to computing that emulates the structure and function of the human brain using specialized hardware and software. It leverages spiking neural networks (SNNs) to process information through events or spikes, offering energy-efficient, real-time computation. By mimicking biological neurons and synapses, neuromorphic systems excel in adaptive learning, sensory processing, and decision-making tasks. This is a paradigm shift in term of Digital Computation based on the Processor and Memory models based on logic that is binary based (as in Von Neumann model).
Neuromorphic computing, offers advantages for AI and Multimodal sensing since by definition it mimics biological neural networks. This allows for low-power, and real time data processing.
History
The following chart provides perspective into the history of Neuromorphic computation.

The table below provides an insight into the different forms of computing.

The segue to Neuromorphic architecture requires both HW and SW changes viz.,
Neuromorphic Hardware :
Relies on asynchronous communication (for scaling and speed)
Does away with clock driven architectures that saves energy
Scaling is done via more hardware tiling rather than increasing clock frequency thereby reducing power consumption
Uses spikes (for power efficiency)
Very parallel, as scaling is done by means of adding more units (cores)
Target low-power
Adaptively Learn
More Accurate, Faster, Lower Power
Neuromorphic Software
Need Algorithms to match the Hardware.
Traditional AI Algorithms like RNN, LSTM etc do not work best for Neuromorphic compute therefore new SW algorithms are required
The following table gives an quick overview of some of the Key Neuromorphic algorithms

Benefits in AI & Sensing
Energy Efficiency
The event driven nature of neuromorphic computing allows only activation based on input data, and therefore reducing idle energy usage.
The analogous nature of inputs and weights, makes multiplications easier and more energy efficient.

Superior Scaling
Enables addition of additional tiles with cores for scaling to greater performance and workloads with minimal impact on power consumption, unlike traditional computing which requires increasing of clock frequency and thereby increasing power consumption
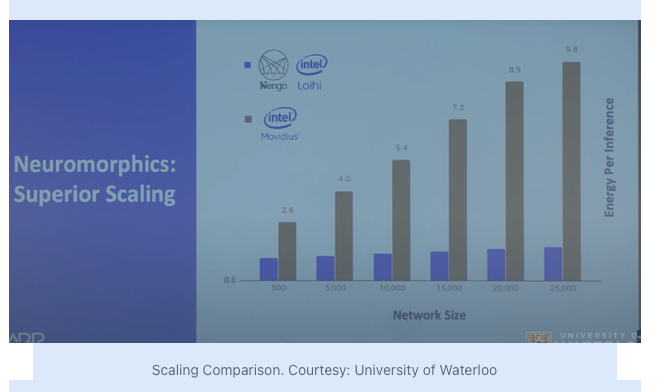
Real Time Processing
Neuromorphic processors handle sensory data efficiently by processing it locally in analogous format, good for latency critical applications
Greater accuracy - Enable greater accuracy at similar power consumption due to adaptive learning benefits
Adaptive Learning - Neuromorphic computing by design (Plasticity) is enabled for adaptive learning
Spike Based Neural Networks
Using spiking neural networks (SNNs), neuromorphic chips process data similar to biological forms in analogous form making it easier for certain tasks, decision-making and complex sensory data analysis.

Segments
Neuromorphic is well suited for the following segments.
Edge AI - are typically fitted wtih multiple forms of sensing, and have RT requirements with low latencies
Automotive - require latency critical handling from multiple sensors viz, LiDAR, RADAR, Vision. Neuromorphics chips can process this effectively
Wearables and Consumer Devices - Wearables and health monitors benefit greatly both from the natural signal processing in analogous format, and the power efficiencies provided
Mobile Devices - ideal for voice, vision and proximity, and gesture sensing.
Use Cases
The following use cases are well enabled by Neuromorphic computing:
Pattern Recognition - Voice analysis, HR/ECG/EEG analysis, Image recognition
Autonomous Systems - Self driving cars, drones, Robotics,
Smart Sensors - IOT Devices
Health Monitoring - EEG/EEG/HR
Gesture Recognition -Advanced Gestures recognition
Challenges and Opportunities
Technological Immaturity - nascent SW ecosystem, programming models and tools
Limited Apps: nice areas like RT and low power tasks
High R&D costs: R&D, prototyping and manufacturing
Early stages of investor funding
Expected Maturity Timeframe
Neuromorphic computing is still in nascent stages, commercial viability might happened over the next 3-5 years, early applications are already emerging in specific segments.
Edge AI ; As early as 2025
AI Acceleration : Supplemental and Replacement systems around end of this decade
Autonomous Systems: Early next decade
Companies
The following Companies are invested in Neuromorphic Computing :
Intel, IBM, BrainChip, Synsense, GrAI Matter, Innatera, BrainLabs, Prophesee, Standford University, SpinNaker
The Future
Neurmorphic Computing promises the existing digital computing paradigm, and promises to be successful for the following reasons:
Energy Efficiency- with the advent of AI, and the enormous power consumption challenges that AI in its current predominant GPU/CPU architecture brings, needs alternatives despite Cerebras and Groq bringing in advances with memory access and its benefits
Real-Time Processing and Adaptability - In particular for sensing (Vision, Sound, Motion, EEG/ECG Waveforms), Gestures making them ideal for Automotive, IOT, Edge, Wearable and Heath segments. They are inherently adaptive, learning from experience with less need for extensive retraining.
Brain like Intelligence evolution: Neuromorphic chips could enable systems via Spike Neural Networks and unsupervised learning. Their capacity to integrate sensing and learning at the hardware makes them more efficient.



